What is a HACCP Decision Tree?
Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point (HACCP) is a way to manage food safety hazards. It is a legal requirement for all food businesses to have a HACCP based food safety management system and it plays an important role in keeping food safe. A HACCP decision tree is a tool that can help you to identify critical control points and act accordingly to reduce or eliminate a food safety hazard.
In this article we will outline what a HACCP decision tree is used for. We will also provide an example of a HACCP decision tree.
What is a HACCP Decision Tree?
A HACCP decision tree is a means to gauge whether a hazard control point is critical or not. A critical control point (CCP) is a step in a process such as during food handling, production or manufacture, at which a control can be applied and is essential to remove or reduce a hazard. A hazard is something that is dangerous and can cause harm. In terms of food safety, a food hazard is something that could make food unsafe to eat.

There are three main types of food safety hazard:
- Microbiological – involving harmful bacteria
- Chemical – involving chemical contamination
- Physical – involving objects getting into food
A HACCP decision tree can help you to identify stages of a process that could be hazardous so that the hazard can be removed or reduced to safe levels.
Want to Learn More?
HACCP is vital to keeping food safe and maintaining high standards of food hygiene. Our range of HACCP Training Courses cover everything you need to know in order to implement effective food safety management.
The Basics of a HACCP Decision Tree
A HACCP decision tree is often presented as a flow chart with a series of questions which helps you to determine CCPs. CCPs can also be determined through experience and judgement, however a decision tree can aid with the identification of them. The number of CCPs in a process will depend on the process itself and its complexity.
To effectively use a HACCP decision tree you must work your way through the questions for each hazard at each process step. The answers to these questions will help you to determine a CCP. It’s important that you keep records of the results of your decision tree and detail the justification for your answers to each question. This will allow you to analyse and repeat the flowchart should any problems arise.

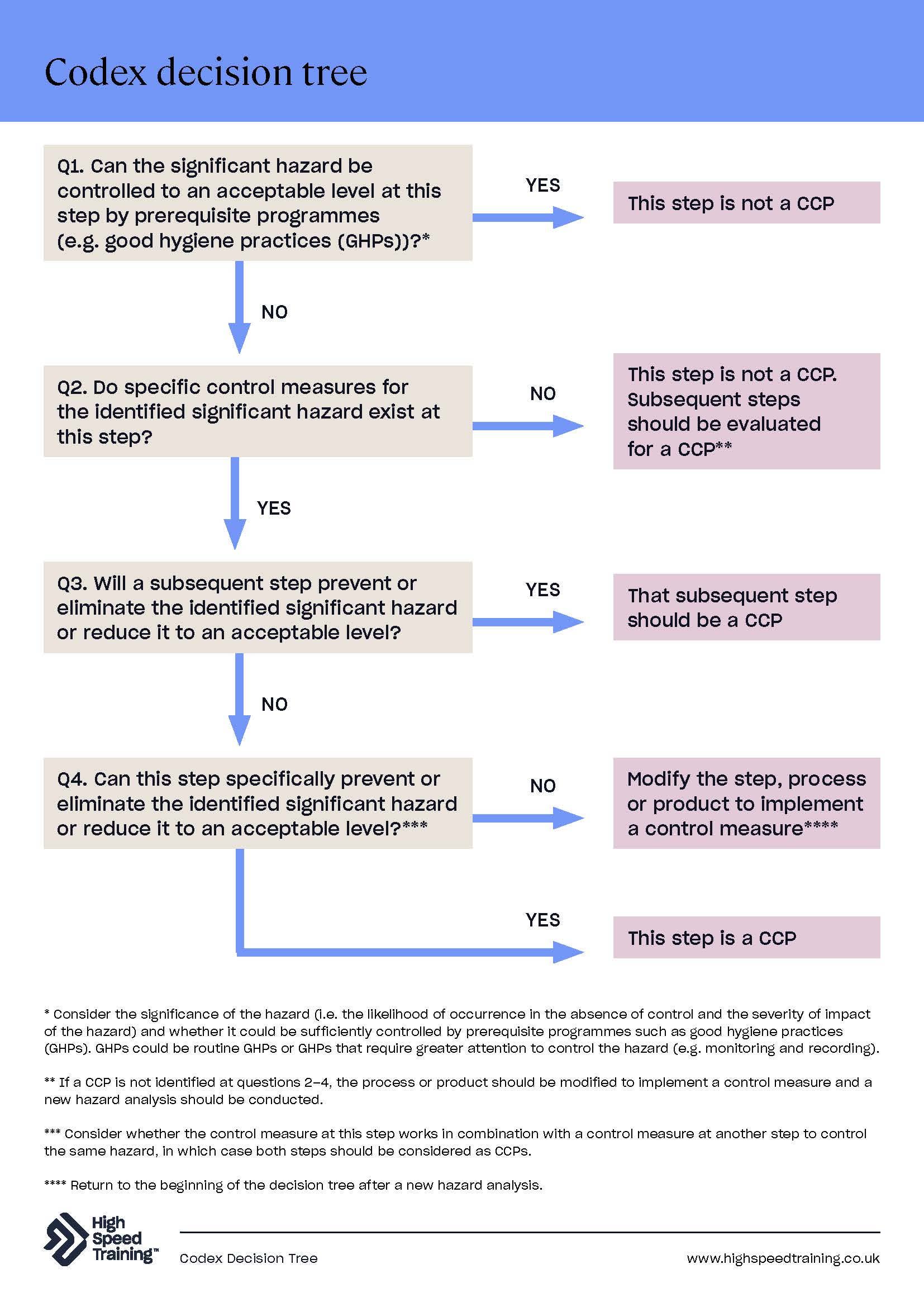
There are many different HACCP decision trees that you can use. The Food Standards Agency’s (FSA) MyHACCP tool focuses on the Codex decision tree and the Campden BRI decision tree, however these are not the only options available and you are not required to use solely those trees. It’s worth noting that the Codex decision tree and the Campden BRI decision tree may determine different CCPs. This is because the Campden BRI decision tree does not identify process steps where hazards are effectively controlled by prerequisite food hygiene requirements as CCPs. Due to this the Codex decision tree typically generates more CCPs than the Campden BRI decision tree.
This is not to say that the Campden BRI decision tree can be used to cut corners as it is predicated on the development and maintenance of prerequisite food hygiene requirements to ensure the continued safe production of food.
Whilst you can use any tree you wish, or devise one yourself, the Codex decision tree was revised and updated by the Codex Alimentarius General Principles of Food Hygiene in 2023 making it the more up-to-date version. The new Codex decision tree reorders previous questions and includes additional questions/guidance from the Campden BRI decision tree. You can find an example of the updated Codex decision tree below.
The Codex Decision Tree
When to Use a HACCP Decision Tree
HACCP decision trees are used when trying to determine whether something is a CCP. This may be after the introduction of a new process, new ingredients or new products which bring with them new risks, or during a regular review of food safety practices.
HACCP is vital to keeping food and by extension the public safe. Whilst personal experience and judgement can be used to identify CCPs, a HACCP decision tree can help to eliminate ambiguity and subsequently facilitate the reduction or elimination of hazards.